OKHttp初探--Call
public interface Call extends Cloneable {
Request request();//返回request对象
Response execute() throws IOException;//执行网络请求,返回Response
void enqueue(Callback responseCallback);//
void cancel();
boolean isExecuted();
boolean isCanceled();
Call clone();
}
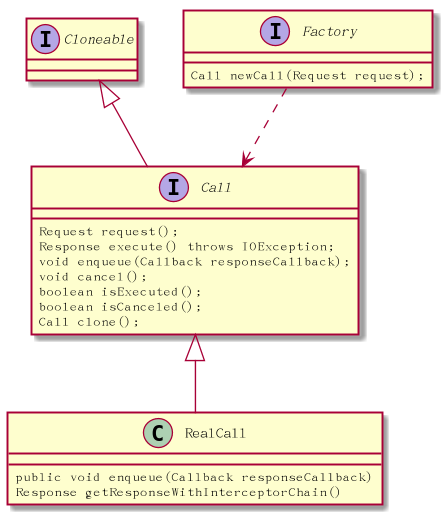
这里面Call有点像Future,有cancel能力。这点是一个重大优势,以往android的请求引擎里不会有cancel功能,cancel都得靠volley,Glide等第三方框架去实现.这是一大进步
RealCall 成员
RealCall是Call的实现类,它的成员有: EventListener 后期要加的模块 OkHttpClient client 通过它可以拿到dispatcher等 RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor retryAndFollowUpInterceptor用来处理cancel的 final Request originalRequest 原请求 final boolean forWebSocket 标记是否用webSocket private boolean executed; 标记是否执行过(只要调用execute方法)
RealCall行为
request() 返回request execute() 执行请求 captureCallStackTrace() 截取调用stack 值得学习! enqueue() 异步执行请求 cancel() 取消 isExecuted() 是否被执行过 streamAllocation() 暂时不知道干啥的 AsyncCall 内部类,用来处理异步请求用到的 redactedUrl() url的摘要,便于打log
重点:execute()
第一章我们讲到: Response response = call.execute();
来分析代码
public Response execute() throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
try {
client.dispatcher().executed(this);
Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (result == null) throw new IOException("Canceled");
return result;
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
1.一个call被多次调execute会抛异常
2.captureCallStackTrace,创建一个Throwable,其实就是记录调用栈
3.client.dispatcher().executed(this);让dispatcher去记录自己的状态
Dispatcher.java
synchronized void executed(RealCall call) {
runningSyncCalls.add(call);
}
4.client.dispatcher().finished(this);让dispatcher移除自己
Dispatcher.java
private <T> void finished(Deque<T> calls, T call, boolean promoteCalls) {
int runningCallsCount;
Runnable idleCallback;
synchronized (this) {
if (!calls.remove(call)) throw new AssertionError("Call wasn't in-flight!");
if (promoteCalls) promoteCalls();
runningCallsCount = runningCallsCount();
idleCallback = this.idleCallback;
}
if (runningCallsCount == 0 && idleCallback != null) {
idleCallback.run();
}
}
getResponseWithInterceptorChain真正的请求实现。
getResponseWithInterceptorChain
通过责任链的设计模式去发请求,后面的章节会详细讲解。
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(
interceptors, null, null, null, 0, originalRequest);
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}