WebSocket的支持
okhttp集成了websocket,使用websocket只需要这样写:
OkHttpClient.Builder builder = new OkHttpClient.Builder();
OkHttpClient client = builder.build();
Request.Builder requestBuilder = new Request.Builder();
requestBuilder.url("ws://192.168.1.101:8888/ws");
final WebSocket webSocket = client.newWebSocket(requestBuilder.build(),
new WebSocketListener() {
@Override
public void onOpen(WebSocket webSocket, Response response) {
super.onOpen(webSocket, response);
webSocket.send("hello websocket");
}
@Override
public void onMessage(WebSocket webSocket, String text) {
super.onMessage(webSocket, text);
}
@Override
public void onMessage(WebSocket webSocket, ByteString bytes) {
super.onMessage(webSocket, bytes);
}
@Override
public void onClosing(WebSocket webSocket, int code, String reason) {
super.onClosing(webSocket, code, reason);
}
@Override
public void onClosed(WebSocket webSocket, int code, String reason) {
super.onClosed(webSocket, code, reason);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(WebSocket webSocket, Throwable t, Response response) {
super.onFailure(webSocket, t, response);
}
});
发送消息给服务器
webSocket.send("hello websocket");
来看底层实现: HttpClient.newWebSocket()调用后会new 一个RealWebSocket
RealWebSocket webSocket = new RealWebSocket(request, listener, new Random());
webSocket.connect(this);
RealWebSocket.java
的构造函数:
public RealWebSocket(Request request, WebSocketListener listener, Random random) {
if (!"GET".equals(request.method())) {//必需要是get请求
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Request must be GET: " + request.method());
}
this.originalRequest = request;
this.listener = listener;
this.random = random;
byte[] nonce = new byte[16];
random.nextBytes(nonce);
this.key = ByteString.of(nonce).base64();//生成一个随机的key后面会成为Sec-WebSocket-Key的Header值
this.writerRunnable = new Runnable() {//起了一个Runnable,无限循环
@Override public void run() {
try {
while (writeOneFrame()) {
}
} catch (IOException e) {
failWebSocket(e, null);
}
}
};
}
connect:
1.先是通过源request创建一个新的request,它会加上一些Header信息:Upgrade,Connection,Sec-WebSocket-Key等
2.创建RealCall发第一次请求
3.当第一次请求返回的时候需要走checkResponse
4.如果checkResponse通过,会告诉listener onOpen
5.初始化Reader和Writer initReaderAndWriter
6.把socket的读取时间设成0,表示没有超时时间,也就是长连接
7.启动loopReader
public void connect(OkHttpClient client) {
client = client.newBuilder()
.protocols(ONLY_HTTP1)
.build();
final int pingIntervalMillis = client.pingIntervalMillis();
final Request request = originalRequest.newBuilder()
.header("Upgrade", "websocket")
.header("Connection", "Upgrade")
.header("Sec-WebSocket-Key", key)
.header("Sec-WebSocket-Version", "13")
.build();
call = Internal.instance.newWebSocketCall(client, request);
call.enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) {
try {
checkResponse(response);
} catch (ProtocolException e) {
failWebSocket(e, response);
closeQuietly(response);
return;
}
// Promote the HTTP streams into web socket streams.
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = Internal.instance.streamAllocation(call);
streamAllocation.noNewStreams(); // Prevent connection pooling!
Streams streams = streamAllocation.connection().newWebSocketStreams(streamAllocation);
// Process all web socket messages.
try {
listener.onOpen(RealWebSocket.this, response);
String name = "OkHttp WebSocket " + request.url().redact();
initReaderAndWriter(name, pingIntervalMillis, streams);
streamAllocation.connection().socket().setSoTimeout(0);
loopReader();
} catch (Exception e) {
failWebSocket(e, null);
}
}
@Override public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
failWebSocket(e, null);
}
});
}
checkResponse:
1.状态码是101表示握手成功,否则就是握手异常
2.Connection的值必需是Upgrade
3.Upgrade的值必需是websocket
4.Sec-WebSocket-Accept的值必需是 ByteString.encodeUtf8(key + WebSocketProtocol.ACCEPT_MAGIC).sha1().base64()
也就是说服务器收到客户端的key,再在基础上加上ACCEPT_MAGIC然后sha1+base64得到的字符
void checkResponse(Response response) throws ProtocolException {
if (response.code() != 101) {
throw new ProtocolException("Expected HTTP 101 response but was '"
+ response.code() + " " + response.message() + "'");
}
String headerConnection = response.header("Connection");
if (!"Upgrade".equalsIgnoreCase(headerConnection)) {
throw new ProtocolException("Expected 'Connection' header value 'Upgrade' but was '"
+ headerConnection + "'");
}
String headerUpgrade = response.header("Upgrade");
if (!"websocket".equalsIgnoreCase(headerUpgrade)) {
throw new ProtocolException(
"Expected 'Upgrade' header value 'websocket' but was '" + headerUpgrade + "'");
}
String headerAccept = response.header("Sec-WebSocket-Accept");
String acceptExpected = ByteString.encodeUtf8(key + WebSocketProtocol.ACCEPT_MAGIC)
.sha1().base64();
if (!acceptExpected.equals(headerAccept)) {
throw new ProtocolException("Expected 'Sec-WebSocket-Accept' header value '"
+ acceptExpected + "' but was '" + headerAccept + "'");
}
}
initReaderAndWriter:
public void initReaderAndWriter(
String name, long pingIntervalMillis, Streams streams) throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
this.streams = streams;
this.writer = new WebSocketWriter(streams.client, streams.sink, random);
this.executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, Util.threadFactory(name, false));
if (pingIntervalMillis != 0) {
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(
new PingRunnable(), pingIntervalMillis, pingIntervalMillis, MILLISECONDS);
}
if (!messageAndCloseQueue.isEmpty()) {
runWriter(); // Send messages that were enqueued before we were connected.
}
}
reader = new WebSocketReader(streams.client, streams.source, this);
}
1.通过scheduleAtFixedRate每过一定的时间发ping
2.如果消息队列(messageAndCloseQueue)不为空就执行一次write
3.初始化WebSocketReader
心跳包之-发ping和接收pong的流程
client发起ping,会收到server的pong,同样server发ping,client会回一个pong
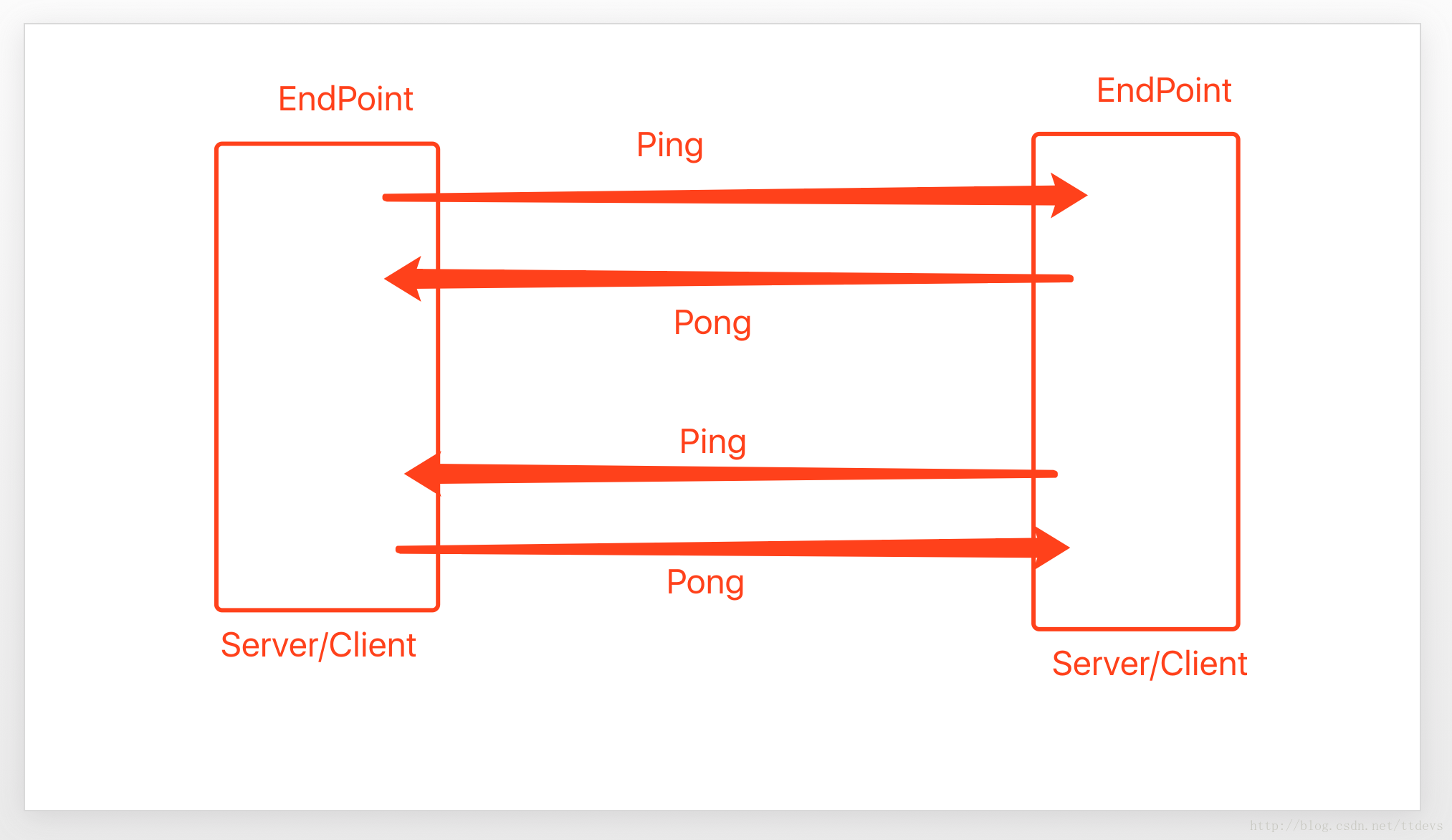
pingRunnable会在executor中每隔一定的时间就执行一次(pingInterval可以配置)
private final class PingRunnable implements Runnable {
PingRunnable() {
}
@Override public void run() {
writePingFrame();
}
}
void writePingFrame() {
WebSocketWriter writer;
synchronized (this) {
if (failed) return;
writer = this.writer;
}
try {
writer.writePing(ByteString.EMPTY);
} catch (IOException e) {
failWebSocket(e, null);
}
}
而pong则是服务器的返回:收到pong的返回,只是pongCount++
@Override public synchronized void onReadPong(ByteString buffer) {
// This API doesn't expose pings.
pongCount++;
}
如果服务器主动发ping会走到onReadPing,此时会把要发的pong加入到Queue,然后启动writer
//作者用了一个Deque来装载所有服务器返回来的pong
private final ArrayDeque<ByteString> pongQueue = new ArrayDeque<>();
public synchronized void onReadPing(ByteString payload) {
// Don't respond to pings after we've failed or sent the close frame.
if (failed || (enqueuedClose && messageAndCloseQueue.isEmpty())) return;
pongQueue.add(payload);
runWriter();
pingCount++;
}
runWriter只是执行了一个writerRunnable
private void runWriter() {
assert (Thread.holdsLock(this));
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(writerRunnable);
}
}
这个writerRunnable会循环执行writeOneFrame,如果返回true的话
this.writerRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
try {
while (writeOneFrame()) {
}
} catch (IOException e) {
failWebSocket(e, null);
}
}
};
writeOneFrame代码
boolean writeOneFrame() throws IOException {
//...ignore code
writer = this.writer;
pong = pongQueue.poll();
if (pong == null) {
messageOrClose = messageAndCloseQueue.poll();
if (messageOrClose instanceof Close) {
//...ignore code 处理Close的消息
this.executor.shutdown();
} else {
//...ignore code
}
}
}
try {
if (pong != null) {
//不为空就写pong
writer.writePong(pong);
} else if (messageOrClose instanceof Message) {
//...ignore code
//处理 message
sink.write(data);
sink.close();
synchronized (this) {
queueSize -= data.size();
}
} else if (messageOrClose instanceof Close) {
//...ignore code处理close
//...ignore code
}
WebSocketReader的loopReader
public void loopReader() throws IOException {
while (receivedCloseCode == -1) {
reader.processNextFrame();
}
}
只要receivedCloseCode==-1就一直执行processNextFrame
1.解析reader
2.读控制类的数据(如ping,pong,close等与业务无关的数据)
3.读消息(与业务相关)
void processNextFrame() throws IOException {
readHeader();
if (isControlFrame) {
readControlFrame();
} else {
readMessageFrame();
}
}
readHeader
private void readHeader() throws IOException {
if (closed) throw new IOException("closed");
// Disable the timeout to read the first byte of a new frame.
int b0;
long timeoutBefore = source.timeout().timeoutNanos();
source.timeout().clearTimeout();
try {
b0 = source.readByte() & 0xff;
} finally {
source.timeout().timeout(timeoutBefore, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
}
opcode = b0 & B0_MASK_OPCODE;//0b00001111
isFinalFrame = (b0 & B0_FLAG_FIN) != 0;//0b10000000
isControlFrame = (b0 & OPCODE_FLAG_CONTROL) != 0;//0b00001000
读第一个byte也就是第一个8位的数,后四位是opcode:
数据包类型(frame type),占4bits
0x0:标识一个中间数据包
0x1:标识一个text类型数据包
0x2:标识一个binary类型数据包
0x3-7:保留
0x8:标识一个断开连接类型数据包
0x9:标识一个ping类型数据包
0xA:表示一个pong类型数据包
0xB-F:保留
isFinalFrame是不是最后一Frame,用第一位来表示
isControlFrame是不是操作Frame
来看看readControlFrame代码
1.处理ping
2.处理pong
3.处理关闭
switch (opcode) {
static final int OPCODE_CONTROL_CLOSE = 0x8;
static final int OPCODE_CONTROL_PING = 0x9;
static final int OPCODE_CONTROL_PONG = 0xa;
}
case OPCODE_CONTROL_PING:
frameCallback.onReadPing(buffer.readByteString());
break;
case OPCODE_CONTROL_PONG:
frameCallback.onReadPong(buffer.readByteString());
break;
case OPCODE_CONTROL_CLOSE:
int code = CLOSE_NO_STATUS_CODE;
//...ignore code
frameCallback.onReadClose(code, reason);
readMessageFrame则是读取数据
private void readMessageFrame() throws IOException {
int opcode = this.opcode;
if (opcode != OPCODE_TEXT && opcode != OPCODE_BINARY) {
throw new ProtocolException("Unknown opcode: " + toHexString(opcode));
}
Buffer message = new Buffer();
readMessage(message);
if (opcode == OPCODE_TEXT) {
frameCallback.onReadMessage(message.readUtf8());
} else {
frameCallback.onReadMessage(message.readByteString());
}
}